
This abstraction layer keeps workloads decoupled from physical platform details, enabling cloud-native delivery flows within the data center and at the edge.

This design allows for a virtually unlimited set of elements in a game, while remaining simple for rulesets which require only a few types of objects.
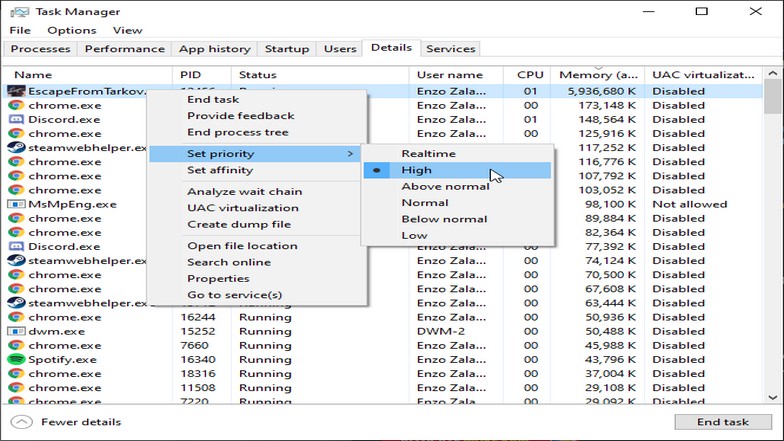
 Parsec’s quality and experience really comes down to the provider. Supercomputers are getting faster than ever, but the next generation, which will be able to do a quintillion floating point You will see whether a game has a 64-bit version if there are two executables, with one having "_圆4" somewhere in the file name, or if you run Windows (10) as your OS, opening Task Manager and going to the Details tab, then right-clicking on one of the column headings (Name, PID, Status, etc) and then adding a column called "Platform" from the list will show you the game's architecture as well if the game is running in the background.Īlso, the amount of RAM that the game uses is determined by the game and the OS, and isn't something that you can change, like for example the priority of the application.Q. If the game is compiled as an 64-bit application, then it can use more than 4GB RAM and will most likely also perform better (faster loading times, less frame-drops, ability to add more effects without a performance impact, etc).
Parsec’s quality and experience really comes down to the provider. Supercomputers are getting faster than ever, but the next generation, which will be able to do a quintillion floating point You will see whether a game has a 64-bit version if there are two executables, with one having "_圆4" somewhere in the file name, or if you run Windows (10) as your OS, opening Task Manager and going to the Details tab, then right-clicking on one of the column headings (Name, PID, Status, etc) and then adding a column called "Platform" from the list will show you the game's architecture as well if the game is running in the background.Īlso, the amount of RAM that the game uses is determined by the game and the OS, and isn't something that you can change, like for example the priority of the application.Q. If the game is compiled as an 64-bit application, then it can use more than 4GB RAM and will most likely also perform better (faster loading times, less frame-drops, ability to add more effects without a performance impact, etc). 
Nothing you can do about this apart from asking the developer to consider compiling a 64-bit version of the game as well.which may or may not require additional programming to the game. If the game is compiled as an 32-bit application, then the 4GB limit is going to stick regardless of the amount of physical RAM in the machine. The memory limitation comes from the way the game is compiled with regards to architecture.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
